OCD Symptoms and Treatment: Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) affects many people worldwide. It involves unwanted thoughts and repetitive behaviors.
Also Read
Understanding OCD is crucial for managing its impact on daily life. OCD can be overwhelming, causing significant distress. Symptoms often include excessive cleaning, checking, or counting. These behaviors aim to reduce anxiety but can take over one’s life. The good news is that effective treatments are available.
Therapy, medication, and self-help strategies can make a big difference. Knowing the symptoms and treatments helps in seeking the proper support. This blog will guide you through the common signs of OCD and explore treatment options. Let’s dive into understanding OCD better.
This blog post serves as a recommendation for knowledge-based content. However, a patient must follow a registered doctor’s instructions.
Credit: www.healyourrootswellness.com
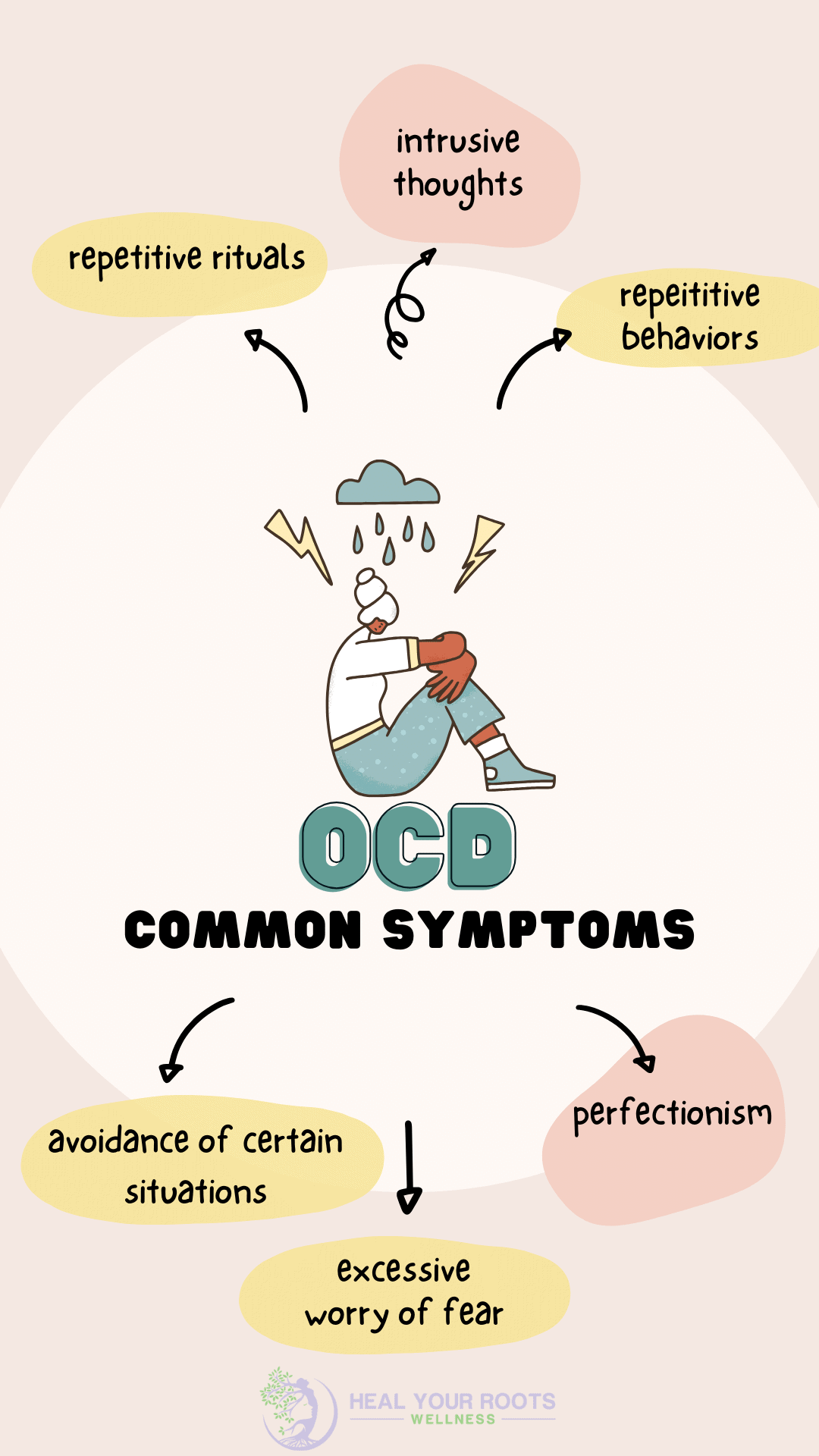
Recognizing OCD Symptoms
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) affects many individuals. Recognizing the symptoms is the first step towards seeking help. This section will help you understand and identify the symptoms of OCD. We will focus on obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors.
Obsessive Thoughts
Obsessive thoughts are unwanted and intrusive. They can cause distress and anxiety. These thoughts often revolve around specific themes. Common themes include:
- Fear of contamination or dirt
- Need for symmetry and order
- Aggressive or horrific thoughts
- Unwanted sexual thoughts
These thoughts can consume a lot of time. They interfere with daily activities. People with OCD often feel they cannot control these thoughts.
Compulsive Behaviors
Compulsive behaviors are repetitive actions. People perform these actions to reduce anxiety caused by obsessive thoughts. Common compulsive behaviors include:
- Excessive hand washing or cleaning
- Arranging items in a specific way
- Repeatedly checking things, like locks or appliances
- Counting or repeating words silently
These behaviors can be time-consuming. They often interfere with social activities and work. People with OCD may feel compelled to perform these actions, even if they know they are unnecessary.
Recognizing OCD symptoms is crucial. It allows individuals to seek proper treatment and support. If you or someone you know exhibits these symptoms, consider reaching out to a healthcare professional.
Causes of OCD
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder, or OCD, affects many people worldwide. Understanding the causes of OCD is key to effective treatment. Researchers believe both genetic and environmental factors play a role in the development of OCD. Let’s explore these factors further.
Genetic Factors
Studies suggest that OCD can run in families. This implies a genetic link. If a family member has OCD, the risk of developing OCD increases. Researchers are looking into specific genes that might be involved. They believe certain genes affect how the brain functions. These changes might lead to OCD symptoms. However, more research is needed to pinpoint the exact genes.
Environmental Influences
Besides genetics, environmental factors can also contribute to OCD. Stressful life events, such as trauma or significant changes, can trigger symptoms. Childhood abuse, neglect, or other traumatic experiences are common triggers. Additionally, infections like streptococcal infections can sometimes cause OCD symptoms. This condition is known as PANDAS (Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal infections). Other factors, like a person’s upbringing and experiences, can also play a role.
Both genetic and environmental factors contribute to the complexity of OCD. Understanding these causes can help in developing effective treatment plans.
Diagnosing OCD
Diagnosing Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) can be challenging. Understanding the symptoms is essential for proper treatment. A detailed evaluation by a professional is often required. Self-assessment tools can also help in recognizing the signs of OCD.
Professional Evaluation
A professional evaluation is crucial for an accurate diagnosis. Mental health professionals use several methods to assess OCD symptoms. Here are some common steps involved:
- Clinical Interviews: A therapist asks detailed questions about thoughts, behaviors, and emotions.
- Diagnostic Criteria: Professionals refer to the DSM-5 for specific criteria.
- Observation: Therapists may observe the individual’s behavior over time.
These steps ensure a comprehensive understanding of the symptoms. Proper diagnosis leads to effective treatment plans.
Self-assessment Tools
Self-assessment tools can help identify OCD symptoms early. These tools are not substitutes for professional diagnosis but can be a helpful first step. Here are some common self-assessment methods:
- Questionnaires: Simple questions about daily habits and thoughts.
- Checklists: Lists of common OCD symptoms to identify personal experiences.
- Online Tests: Interactive tests that provide immediate feedback.
Using these tools can help individuals recognize the need for professional help. Early detection leads to better management of OCD symptoms.

Credit: continentalhospitals.com
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a proven treatment for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). It works by addressing the thoughts and behaviors that contribute to OCD. The therapy helps patients learn new ways to think and act. This approach can significantly reduce OCD symptoms. Below, we will explore key components and benefits of CBT.
Exposure And Response Prevention (ERP)
Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP) is a core part of CBT for OCD. This method involves exposing patients to their fears in a controlled way. The goal is to help them face their anxieties without engaging in compulsive behaviors. For example, a person afraid of germs may touch a doorknob without washing their hands. Over time, this process reduces fear and anxiety.
ERP consists of two main steps:
- Exposure: Facing fears in a gradual, controlled manner.
- Response Prevention: Avoiding compulsive behaviors that follow exposure.
Patients practice these steps repeatedly. Consistent practice helps reduce the power of OCD over time.
Benefits Of Cbt
The benefits of CBT for OCD are extensive:
- Reduced Symptoms: Patients often experience a significant drop in OCD symptoms.
- Improved Quality of Life: Less anxiety and fewer compulsions lead to a better daily life.
- Long-Term Results: CBT provides skills that help maintain progress over time.
- No Medication Required: CBT can be effective without the need for medication.
- Personal Empowerment: Patients gain control over their thoughts and actions.
CBT is a structured, effective approach to treating OCD. It focuses on teaching practical skills. These skills help patients manage their condition independently.
Medication Options
Managing Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) often involves a combination of treatments. Medication is a key option for many. It helps reduce symptoms and improve daily life. Here, we’ll explore some common medications used to treat OCD.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (ssris)
SSRIs are the most commonly prescribed medications for OCD. They work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that affects mood and anxiety.
Common SSRIs include:
- Fluoxetine (Prozac)
- Sertraline (Zoloft)
- Paroxetine (Paxil)
- Fluvoxamine (Luvox)
- Citalopram (Celexa)
These medications often take several weeks to show effects. Patience is key during this period.
Possible Side Effects
While SSRIs can be effective, they may have side effects. Common side effects include:
- Nausea
- Headache
- Dry mouth
- Insomnia
- Sexual dysfunction
It’s important to discuss any side effects with your doctor. They can adjust the dosage or try a different medication if needed.
In some cases, a combination of medications may be required. This can help to manage both symptoms and side effects more effectively.
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can help manage OCD symptoms. Simple adjustments in daily life can make a big difference. By focusing on healthy habits, one can reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress can trigger OCD symptoms. It’s important to find ways to manage it. Deep breathing exercises can help calm the mind. Practicing mindfulness can also be useful. It helps to stay present and reduce anxious thoughts. Regular physical activity, such as walking or yoga, can lower stress levels too.
Healthy Routines
Maintaining a healthy routine supports mental health. Eating balanced meals provides the body with needed nutrients. This can improve mood and energy levels. Getting enough sleep is crucial as well. A good night’s rest helps the mind to function better. Establishing a regular sleep schedule can be beneficial.
Staying organized can also help. Keeping a clean and orderly environment reduces stress. Setting small, achievable goals can provide a sense of accomplishment. This can boost self-esteem and motivation.
Support Systems
Support systems play a crucial role in managing OCD symptoms. They provide emotional and practical help. A strong support system can make daily challenges easier. Let’s explore the key elements of support systems.
Therapy Groups
Therapy groups offer a safe space to share experiences. Members understand each other’s struggles. This connection reduces feelings of isolation. Group therapy often includes structured activities. These activities help in developing coping strategies. Members learn from each other’s successes and setbacks.
Family And Friends
Family and friends are vital in supporting someone with OCD. They offer emotional support and understanding. Loved ones can help with managing daily tasks. Their encouragement boosts confidence. It’s important for them to stay informed about OCD. This knowledge allows them to provide better support.
Credit: www.africa-ird.org
Innovative Treatments
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a challenging condition. Traditional treatments include therapy and medication. But innovative treatments are emerging to help those affected. These treatments offer new hope and alternatives. In this section, we will explore two such treatments.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (tms)
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive treatment. It uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. This treatment is used for depression and now for OCD too. It targets specific areas of the brain involved in OCD.
The procedure involves placing a magnetic coil on the scalp. Pulses of magnetic energy are sent to the brain. This process aims to reduce OCD symptoms. TMS is done in a doctor’s office. Each session lasts about 30 to 60 minutes. Patients may need multiple sessions over several weeks.
TMS has shown promising results. Many patients report a decrease in symptoms. It is safe and has few side effects. Common side effects include headaches and scalp discomfort. These are usually mild and temporary.
Emerging Therapies
New therapies for OCD are being developed. These emerging therapies offer fresh approaches to treatment. Some focus on technology, while others use new techniques.
One such therapy is Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS). DBS involves implanting electrodes in the brain. These electrodes send electrical impulses to targeted areas. This can help regulate abnormal brain activity linked to OCD.
Another promising therapy is Virtual Reality (VR) Exposure Therapy. VR therapy uses virtual environments to expose patients to their fears. This helps them confront and manage their OCD symptoms in a controlled setting. VR therapy is immersive and can be tailored to each patient.
Researchers are also exploring the use of Ketamine for OCD. Ketamine is a medication traditionally used for anesthesia. Recent studies show it may reduce OCD symptoms quickly. It is still in the experimental stage but shows potential.
These emerging therapies provide new options for those with OCD. They offer hope for better management of symptoms. As research continues, more innovative treatments will likely emerge.
Long-term Management
Managing Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a continuous journey. The key is to maintain progress and prevent relapse. Long-term management involves lifestyle changes, therapy, and self-care. This section will guide you through effective strategies for managing OCD in the long run.
Maintaining Progress
Maintaining progress is crucial for anyone with OCD. Here are some strategies:
- Regular therapy sessions: Continue seeing a therapist to stay on track.
- Medication adherence: Take prescribed medication as directed by your doctor.
- Support groups: Join support groups to share experiences and gain support.
- Mindfulness practices: Engage in mindfulness and relaxation techniques.
Consistency is key. Regularly practicing these strategies helps in sustaining progress.
Preventing Relapse
Preventing relapse requires vigilance and proactive measures. Consider the following:
- Recognize triggers: Identify and understand your personal triggers.
- Develop coping skills: Learn and use effective coping mechanisms.
- Stay connected: Keep in touch with your support network.
- Self-care: Prioritize self-care and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Relapse can be part of the process. Being prepared can help you manage it effectively.
| Maintaining Progress | Preventing Relapse |
|---|---|
| Regular therapy sessions | Recognize triggers |
| Medication adherence | Develop coping skills |
| Support groups | Stay connected |
| Mindfulness practices | Self-care |
More Tips: OCD Symptoms and Treatment
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a mental health condition. It causes cycles of intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors. For many, it begins subtly, growing into a pattern that disrupts daily life. Learning about OCD symptoms and treatment is essential for managing the condition and improving quality of life.
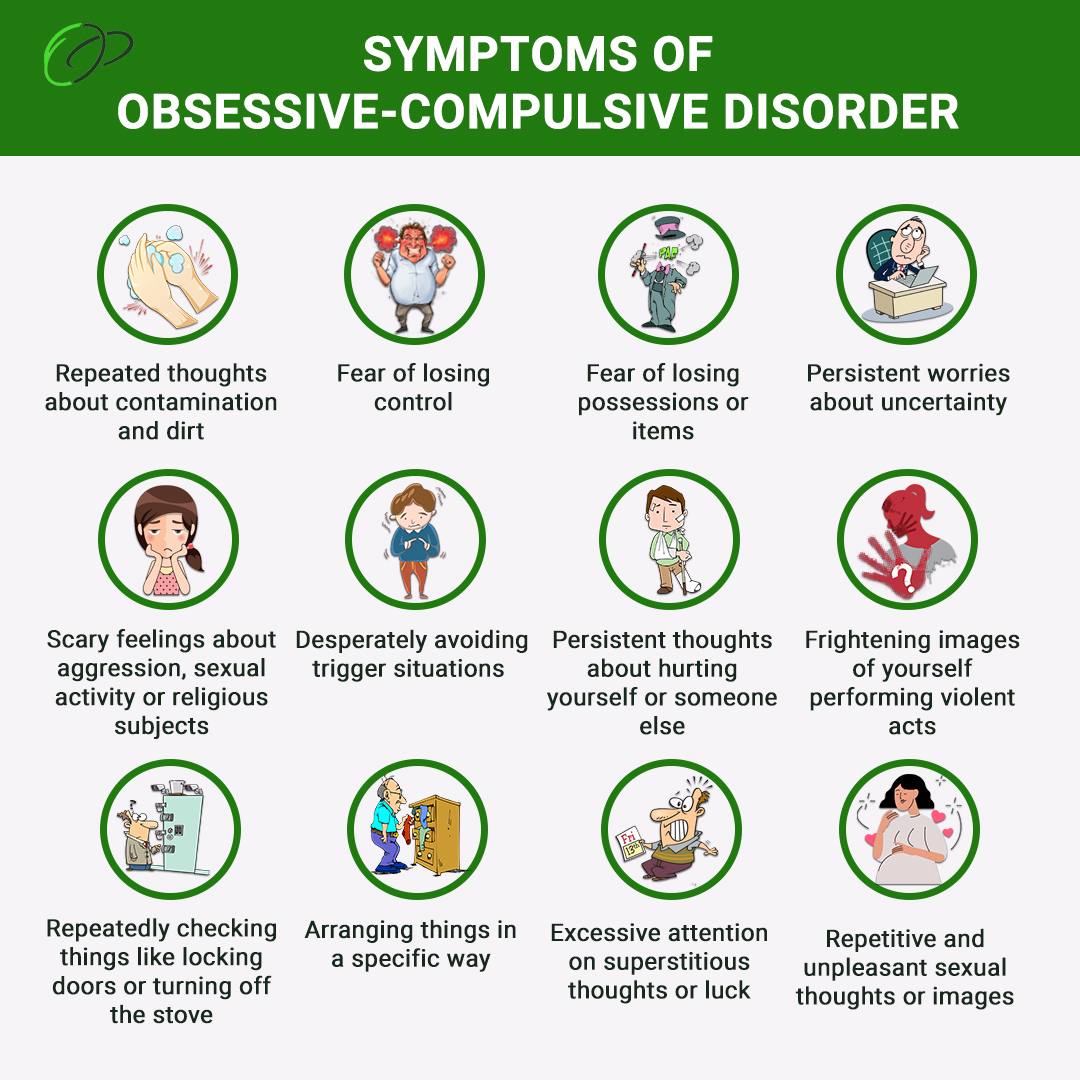
Common Symptoms of OCD
OCD often combines two key elements: obsessions and compulsions. Unwanted thoughts, images, or urges trigger distress, and we call these obsessions. These might include fears of germs, doubts about safety, or disturbing ideas.
Compulsions are actions that ease the distress of obsessions. They include cleaning, counting, and checking many times.
For example, a fear of contamination might cause excessive handwashing. Another may check locks many times before leaving home, even when they know it’s secure. These symptoms vary widely but interfere with work, relationships, and personal well-being. Recognizing signs of OCD in adults or children is often the first step toward seeking help.
Triggers and Co-occurring Conditions
OCD does not exist in isolation. It is often linked to anxiety and depression, forming a cycle where each condition worsens the other. Some experience specific OCD triggers, such as stress, trauma, or even minor life changes. For many, the OCD and anxiety connection makes daily challenges feel overwhelming.
Co-occurring issues like substance abuse or physical health concerns can complicate recovery. Addressing these co-occurring conditions as part of a treatment plan ensures a holistic approach to wellness.
Effective OCD Treatments
OCD is manageable with the right combination of therapy, medication, and self-help strategies. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for OCD, specifically Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP), is highly effective. ERP involves facing obsessions without engaging in compulsions, breaking the cycle over time.
Medication is another option, with SSRIs like fluoxetine commonly prescribed. These medications help balance brain chemistry, reducing the intensity of symptoms. For those seeking alternative solutions, natural remedies for OCD, such as mindfulness practices or yoga, can provide added relief.
Practical Strategies for Living with OCD
Living with OCD requires practical tools to handle daily challenges. The 3-3-3 rule for anxiety is a grounding technique that can help during moments of high stress. It involves identifying three things you see, hear, and move, anchoring you to the present moment.
Joining support groups for OCD patients can also be beneficial. These groups provide a space to share experiences and learn from others who understand the journey. Success stories of overcoming OCD remind us that progress is possible with the right support and persistence.
Finding Hope in the Journey
Many ask, “Can OCD be treated without medication?” While medication helps many, therapy and self-help are powerful tools for recovery. The path to healing may feel slow. But, small steps can help a lot. Coping strategies and seeking help are good examples. Whether exploring best treatments for OCD or learning from success stories, every effort contributes to regaining control over life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Common OCD Symptoms?
Common OCD symptoms include repetitive thoughts, compulsive behaviors, and extreme anxiety. Sufferers often engage in rituals to reduce anxiety.
How Is Ocd Diagnosed?
OCD is diagnosed through clinical evaluation by a mental health professional. Symptoms must be persistent and interfere with daily life.
What Treatments Are Available For OCD?
Treatments for OCD include cognitive-behavioral therapy and medication. Exposure and response prevention is a key technique in therapy.
Can OCD Be Cured?
OCD cannot be cured, but symptoms can be managed effectively with treatment. Many people experience significant improvement.
Conclusion
Understanding OCD symptoms and treatments can change lives. Early diagnosis is crucial. Seek professional help if symptoms arise. Treatments include therapy and medication. Lifestyle changes also support recovery. Support systems play a key role. Awareness spreads hope and understanding. Everyone deserves a chance to live well.
Always prioritize mental health. Take steps towards a healthier mind today.