Types of Eating Disorders: Eating disorders affect millions of people worldwide. They often have serious physical and emotional impacts.
Also Read
Understanding the different types can help in recognizing and addressing these disorders. Eating disorders are complex mental health conditions that involve unhealthy relationships with food and body image.
They can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background. These disorders often stem from a combination of genetic, psychological, and environmental factors.
Recognizing the signs early can lead to better outcomes and support. In this blog post, we’ll explore various types of eating disorders, shedding light on their symptoms and potential treatments.
By increasing awareness, we hope to promote better understanding and encourage those affected to seek help. Let’s dive into the different types and their unique characteristics.
Introduction To Eating Disorders
Eating disorders are serious medical conditions. They affect a person’s eating habits. These disorders can lead to severe health problems. They impact physical and mental health. Recognizing the signs early can make a big difference.
Prevalence And Impact
Eating disorders are common worldwide. Millions of people suffer from them. They can affect anyone. Both men and women experience them. Young and old can be affected. These disorders can lead to life-threatening conditions. Heart disease and kidney failure are just a few examples. They also impact mental health. Anxiety and depression often occur together. Early treatment is crucial.
Common Misconceptions
Many people misunderstand eating disorders. Some think they are just about food. This is not true. They are complex conditions. They involve emotional and psychological issues. Others believe only young women get them. This is also false. Eating disorders affect all genders and ages. Another myth is that people choose to have them. In reality, they are serious illnesses. They need proper treatment and support.
Credit: fherehab.com
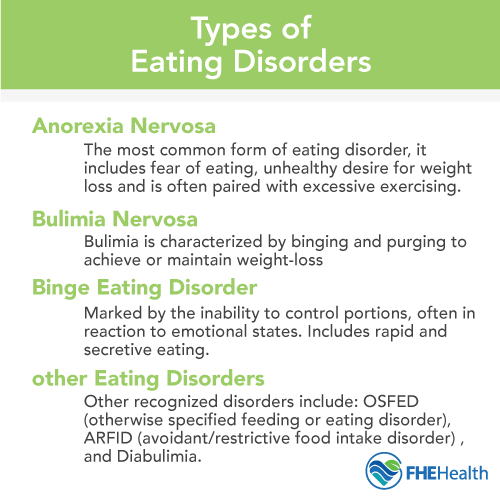
Anorexia Nervosa
Anorexia Nervosa is a serious eating disorder. It is marked by extreme weight loss. People with anorexia have a distorted body image. They see themselves as overweight even when they are underweight. This disorder can have severe health consequences.
Symptoms And Signs
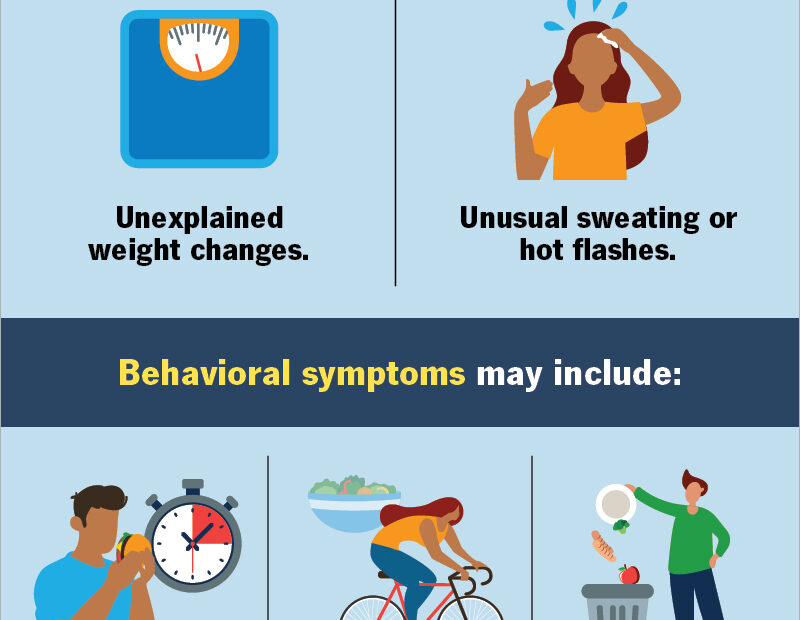
Individuals with anorexia may exhibit several symptoms. They often have an intense fear of gaining weight. They may restrict their food intake drastically. Some may engage in excessive exercise. They may also use laxatives or diuretics. Physical signs include extreme thinness and brittle hair. Other signs are dry skin, and a lack of energy. People with anorexia may also withdraw from social activities.
Health Risks
Anorexia poses many health risks. It can lead to severe malnutrition. This affects the entire body. The heart can suffer from irregular rhythms. Blood pressure may drop dangerously low. Bones can become weak and brittle. This increases the risk of fractures. Anorexia can also cause organ damage. The brain may suffer, leading to cognitive issues. In extreme cases, it can be fatal. Early treatment is crucial to prevent these risks.
Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia Nervosa is a serious eating disorder. It involves cycles of binge eating followed by purging. This behavior can harm both the body and mind. Understanding the symptoms and consequences is crucial.
Binge-purge Cycle
People with Bulimia Nervosa often feel a loss of control during binge eating. They consume large amounts of food in a short time. This is followed by feelings of guilt or shame. To counteract these feelings, they engage in purging behaviors.
Purging can include:
- Self-induced vomiting
- Excessive use of laxatives
- Fasting
- Excessive exercise
This cycle can become very harmful over time. The body and mind both suffer from this repetitive behavior.
Physical And Emotional Consequences
The physical effects of Bulimia Nervosa can be severe. Common issues include:
| Physical Consequences | Details |
|---|---|
| Electrolyte Imbalance | Can lead to irregular heartbeats and heart failure |
| Gastrointestinal Problems | Chronic constipation or diarrhea |
| Dental Issues | Erosion of tooth enamel from frequent vomiting |
| Dehydration | Due to fluid loss during purging |
Emotionally, Bulimia Nervosa can cause:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Low self-esteem
- Feelings of shame and guilt
These emotional struggles often reinforce the binge-purge cycle. It’s important to seek help to break this cycle.
Binge Eating Disorder
Binge Eating Disorder (BED) is a serious mental health condition. It involves recurrent episodes of eating large quantities of food. Unlike other eating disorders, people with BED do not engage in purging behaviors. This disorder can lead to significant physical and emotional problems.
Characteristics
The key characteristics of Binge Eating Disorder include:
- Eating unusually large amounts of food in a short period.
- Feeling a lack of control during binge episodes.
- Eating rapidly during binge episodes.
- Eating until uncomfortably full.
- Eating alone due to embarrassment.
- Feeling disgusted, depressed, or guilty after binge eating.
These behaviors occur at least once a week for three months or more.
Associated Health Issues
Binge Eating Disorder is linked to various health issues. Some of the most common include:
- Obesity: Many people with BED are overweight or obese.
- Heart disease: Higher risk due to poor diet and obesity.
- Type 2 diabetes: Increased risk due to weight gain.
- High blood pressure: Common in individuals with BED.
- Gastrointestinal problems: Issues like acid reflux and stomach pain.
- Mental health issues: Depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
Early treatment is crucial to manage these health risks.
Avoidant/restrictive Food Intake Disorder (arfid)
Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID) is a serious eating disorder. It involves limitations in the amount or types of food consumed. Unlike other eating disorders, ARFID does not involve distress about body shape or size. People with ARFID may avoid food due to sensory issues, fear of choking, or lack of interest in eating. This disorder can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. Understanding ARFID is crucial for providing the right support and treatment.
Key Features
ARFID has several distinct features. People with ARFID often have a limited range of foods they eat. They may avoid foods based on texture, smell, or color. Fear of choking or vomiting can also be a reason for avoidance. Unlike other eating disorders, ARFID is not linked to body image concerns. It often leads to significant nutritional deficiencies and weight loss. Individuals with ARFID may also have anxiety around meals.
Potential Complications
ARFID can lead to many health issues. Nutritional deficiencies are common due to limited food intake. This can cause anemia, weak bones, and poor growth in children. Weight loss can become severe, leading to malnutrition. Social issues may arise as well. Eating in public or with others can cause anxiety and stress. This can lead to isolation and impact relationships. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to manage ARFID effectively.
Other Specified Feeding Or Eating Disorder (osfed)
Other Specified Feeding or Eating Disorder (OSFED) is a category used to diagnose eating disorders that do not meet the criteria for other specific disorders. This category includes behaviors that cause significant distress and impairment. Individuals with OSFED often experience severe emotional, physical, and social challenges.
Defining Traits
OSFED encompasses a range of symptoms that vary widely. These symptoms can be just as serious as those of other eating disorders. Common traits include:
- Disordered eating patterns
- Extreme concern with body weight or shape
- Frequent episodes of eating very little or large amounts of food
- Feelings of guilt or shame after eating
Examples
OSFED includes several subtypes, each with unique characteristics. Some examples are:
| Subtype | Description |
|---|---|
| Atypical Anorexia Nervosa | All symptoms of anorexia nervosa, but the individual’s weight is within or above normal range. |
| Binge Eating Disorder (BED) of Low Frequency | Episodes of binge eating occur less frequently than once a week or for less than three months. |
| Purging Disorder | Recurrent purging to control weight or shape without binge eating episodes. |
| Night Eating Syndrome | Excessive food consumption in the evening or night, leading to distress and impairment. |
Each subtype of OSFED presents unique challenges. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for seeking timely help.
Causes And Risk Factors
Eating disorders are complex conditions. They stem from a mix of factors. Understanding these factors helps in early intervention and treatment. Here, we explore the main causes and risk factors.
Genetic Influences
Genetics play a crucial role in eating disorders. Studies show that these disorders run in families. If a parent or sibling has an eating disorder, the risk increases.
Some genetic traits can make people more prone. For example, traits like perfectionism and sensitivity. These can increase the risk of developing an eating disorder.
Research suggests that certain genes affect how the brain regulates food intake. They also affect body weight and mood.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors are just as important. Social pressures, especially about body image, can lead to eating disorders. Media often promotes thinness, impacting self-esteem.
Family dynamics also play a role. Overly critical or controlling family environments can increase risk. Trauma or abuse in childhood is another significant factor.
Peers influence eating behaviors too. Friends and social circles set norms about diet and appearance. This peer pressure can contribute to unhealthy eating habits.
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Family History | Increases genetic risk |
| Social Media | Promotes unrealistic body images |
| Peer Pressure | Influences eating behaviors |
Understanding these factors can help in identifying early signs. Early detection leads to better outcomes.

Credit: www.honeylake.clinic
Treatment And Support
Eating disorders are serious conditions. They require proper treatment and support. Treatment can vary based on the type of eating disorder. Support is vital for recovery. Here are some common approaches and support systems.
Therapeutic Approaches
Treatment for eating disorders often includes therapy. Therapy helps address the root causes. Here are some common therapeutic approaches:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps change negative thought patterns. It is effective for many eating disorders.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT focuses on emotional regulation. It teaches coping skills.
- Family-Based Therapy (FBT): FBT involves family members in the treatment. It is often used for younger patients.
- Interpersonal Therapy (IPT): IPT addresses relationship issues. It helps improve social functioning.
Support Systems
Support systems play a crucial role in recovery. They provide emotional and practical help. Here are some common support options:
- Support Groups: Joining a support group can be beneficial. Members share experiences and offer encouragement.
- Online Communities: Online forums and groups provide support. They offer a sense of community and understanding.
- Friends and Family: Loved ones can offer daily support. They help create a positive environment.
- Healthcare Providers: Regular check-ups with doctors and therapists are important. They monitor progress and adjust treatment plans.
Both therapy and support systems are essential. They work together to help individuals recover and lead healthy lives.
Prevention And Awareness
Preventing eating disorders involves understanding and addressing the root causes. Awareness plays a crucial role in recognizing early signs. By educating people, we can help reduce the prevalence of these disorders. Let’s explore some key strategies.
Educational Initiatives
Educational initiatives can significantly help in preventing eating disorders. Schools and communities should focus on mental health education. This education should include information about eating disorders.
Here are some ways to implement educational initiatives:
- Workshops and seminars on healthy eating habits
- Incorporating mental health education into school curriculums
- Training teachers to identify early signs of eating disorders
- Providing resources and support for students and parents
By equipping people with knowledge, we can empower them to make healthier choices.
Promoting Healthy Relationships With Food
Promoting a healthy relationship with food is essential. It’s important to teach that food is not the enemy. Healthy eating habits should be encouraged without promoting fear or guilt.
Consider these strategies to promote a healthy relationship with food:
- Encourage balanced meals that include a variety of foods
- Avoid labeling foods as “good” or “bad”
- Model healthy eating behaviors
- Focus on the importance of nutrition, not just weight
Creating a positive food environment can help prevent disordered eating.
Prevention and awareness are key to combating eating disorders. Through educational initiatives and promoting healthy relationships with food, we can make a significant impact.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/eating-disorder-5200354-DD-Final-c0a1c0ab5fcf4ddbb2457a87b3acfd8f.jpg)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Main Types Of Eating Disorders?
The main types are anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder. Each has unique symptoms and health risks. Early detection and treatment are crucial for recovery.
How Is Anorexia Nervosa Characterized?
Anorexia nervosa is characterized by extreme food restriction, fear of gaining weight, and a distorted body image. It leads to severe weight loss and health issues.
What Are Symptoms Of Bulimia Nervosa?
Bulimia nervosa involves cycles of binge eating and purging. Symptoms include eating large amounts, then using vomiting or laxatives to avoid weight gain.
How Does Binge-eating Disorder Differ?
Binge-eating disorder involves consuming large quantities of food without purging. It leads to obesity and related health problems. Emotional distress often accompanies episodes.
Conclusion
Understanding different types of eating disorders is crucial for awareness. Each disorder has unique symptoms and challenges. Early detection can lead to better outcomes. Seek professional help if needed. Support from loved ones plays a vital role. Remember, recovery is possible with the right resources.
Stay informed and compassionate. Your awareness can make a difference.


Hey There. I found your weblog the usage of msn. This is a really neatly written article. I抣l make sure to bookmark it and come back to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the post. I will definitely comeback.
Thanks for the sensible critique. Me and my neighbor were just preparing to do a little research about this. We got a grab a book from our local library but I think I learned more from this post. I’m very glad to see such fantastic information being shared freely out there.
hello there and thank you to your info ?I抳e definitely picked up something new from proper here. I did however experience several technical points using this website, as I skilled to reload the site many instances previous to I may just get it to load properly. I had been brooding about if your web host is OK? Not that I am complaining, but slow loading instances occasions will often affect your placement in google and could injury your quality rating if advertising and ***********|advertising|advertising|advertising and *********** with Adwords. Anyway I抦 including this RSS to my e-mail and could glance out for a lot extra of your respective intriguing content. Make sure you update this once more soon..
I was more than happy to find this web-site.I needed to thanks in your time for this glorious read!! I positively having fun with every little bit of it and I’ve you bookmarked to take a look at new stuff you weblog post.
I adore your wp web template, wherever did you download it from?